Setting the right price for your product is as essential to the success of any business as breathing is to life, as it directly impacts sales, profitability, and market positioning. In fact, pricing is often considered one of the most important factors in a customer's purchasing decision.
According to a study by McKinsey & Company , 60% of companies use market research to set their product prices, highlighting the importance of understanding both cost structures and consumer behavior. Moreover, research shows that small pricing adjustments can have a significant impact on demand; for example, pricing ending in ".99" has been shown to increase sales by up to 24%, according to the Journal of Consumer Research.
In this context, business owners need to balance a variety of factors, including;
Market demand
By using strategic pricing methods—such as cost-plus, competitive, or value-based pricing—businesses can optimize their pricing strategy to not only cover costs but also maximize profitability and customer satisfaction.
Here are some key statistics and strategies to guide the pricing process:
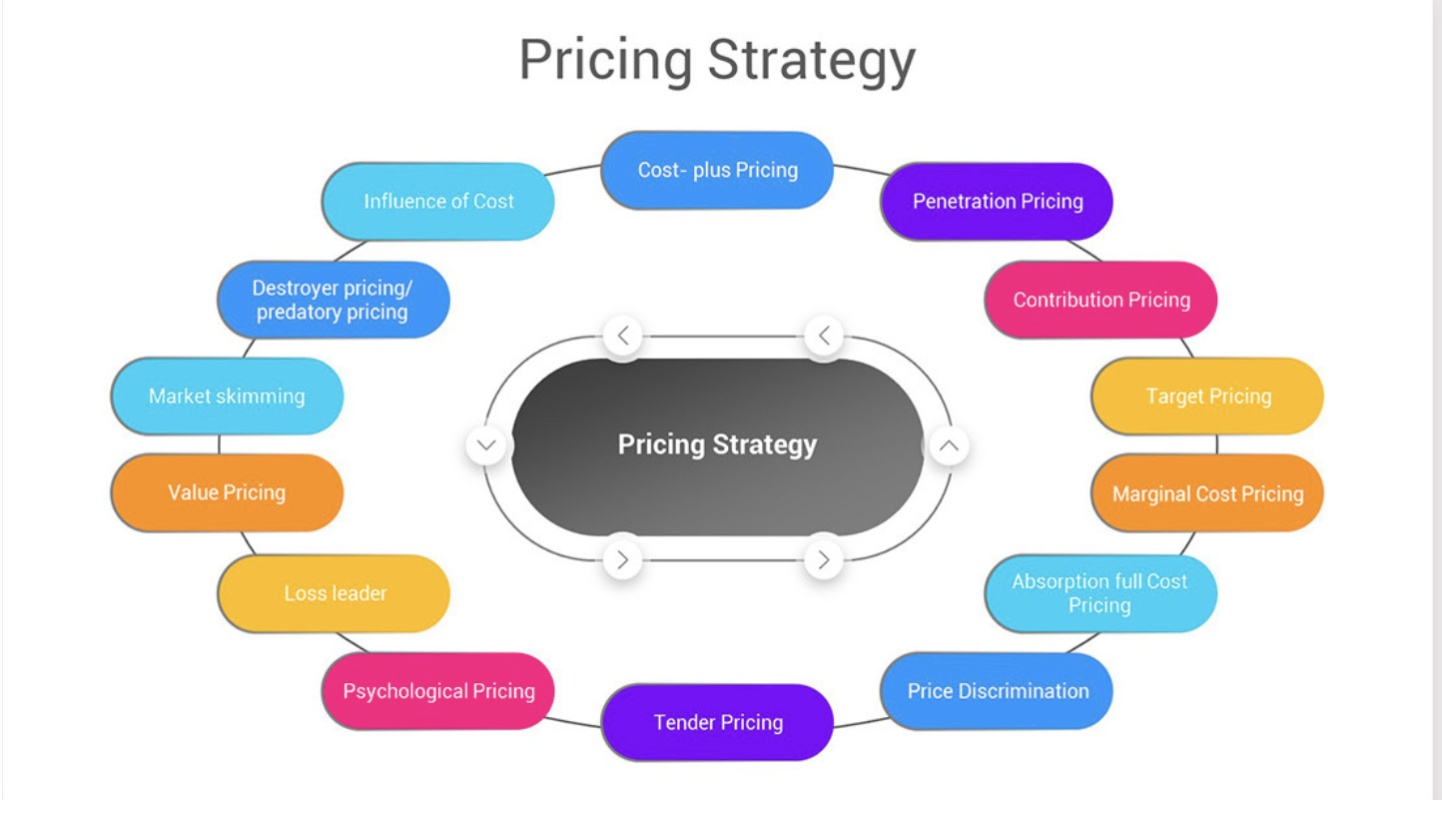
1. Cost-Plus Pricing
According to the National Association for the Self-Employed (NASE) , businesses often use cost-plus pricing, where the selling price is based on the cost of production plus a markup. For example, if the cost to produce an item is Ksh 500 and the desired markup is 50%, the product would be priced at Ksh 750.
This ensures that the business covers its costs and earns a profit. By adding a markup percentage to the production cost, businesses can not only recover the expenses associated with manufacturing the product but also generate enough profit to sustain operations, invest in growth, and fund other business activities
2. Market Research
Market research is crucial for determining the optimal price of a product. According to a survey by McKinsey & Company, 60% of companies use market research to analyze competitors' prices and customer preferences.
This research involves collecting data on what similar products are priced at, understanding customer behavior, and identifying trends in the market. By knowing what customers are willing to pay and how your product compares to others in terms of features, quality, and brand reputation, you can set a price that attracts customers while staying competitive. Additionally, it helps in identifying pricing opportunities, such as niche markets or underpriced competitors.
3. Price Elasticity of Demand
The price elasticity of demand measures how sensitive customers are to price changes. A study from the Journal of Marketing Research found that for many products, a 1% increase in price could result in a 0.5% to 1% decrease in demand. However, luxury goods and products with fewer substitutes often have lower elasticity, meaning price increases do not significantly impact demand.
By understanding elasticity, businesses can determine the most effective pricing strategy—whether to increase prices for higher profit margins or lower them to boost sales. For example, in cases where demand is highly elastic, even small price changes can lead to significant shifts in purchasing behavior.
4. Psychological Pricing
Psychological pricing is a strategy that uses pricing techniques to influence consumer perception. A study by the Journal of Consumer Research showed that prices ending in ".99" (e.g., Ksh 1,999 instead of Ksh 2,000) can lead to up to a 24% increase in sales due to the "left-digit effect," where consumers perceive Ksh 1,999 as significantly cheaper than Ksh 2,000. This small change in price creates the illusion of a better deal and often drives purchasing decisions.
Other tactics include offering price bundles or using "charm prices" that are just below a round number. These psychological factors can be a powerful tool, especially when targeting price-sensitive consumers.
5. Competitive Pricing
Competitive pricing involves setting a price based on the prices of similar products in the market. According to research by Price Intelligently , 74% of companies take competitor pricing into account when determining their own. This strategy can involve pricing at a similar level to competitors, offering a slightly lower price to attract price-sensitive customers, or positioning the product as a premium offering with a higher price.
By analyzing competitors, businesses can spot opportunities for differentiation, such as offering better features, customer service, or quality. This helps businesses set a competitive price that appeals to their target audience while ensuring profitability.
6. Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing focuses on the perceived value of a product to the customer rather than its production cost. According to Harvard Business Review , businesses that use this pricing model can often increase their prices by 20–30% without negatively affecting demand, as long as customers perceive the product as offering high value. For example, a software company might price its product higher because customers view it as a time-saver or an essential tool for their business.
This strategy works well when the product provides unique benefits, features, or brand recognition. By emphasizing the value customers receive, businesses can justify higher prices while enhancing customer loyalty.
7. Discounting and Promotions
Discounting and promotions can drive sales, but they must be used strategically. According to Nielsen , 48% of consumers in Kenya say they frequently buy products on sale. However, over-relying on discounts can erode a product's perceived value, especially if the product is consistently marked down.
For example, frequent sales might suggest that the product is overpriced to begin with or that it’s of lower quality. Instead, businesses should use discounts selectively, such as for seasonal promotions or loyalty programs, to maintain brand perception and encourage repeat customers. Strategic promotions, like offering discounts on first-time purchases or bundling products, can also increase customer lifetime value without devaluing the brand.
Key Takeaways for Pricing Strategy:
Understand your costs (both fixed and variable) to avoid underpricing and ensure profitability. For instance, consider the cost of production, marketing, and distribution when calculating your price.
Study competitors’ prices to identify opportunities for differentiation or areas where you can offer a competitive advantage. Competitor research can also reveal pricing gaps where your product can stand out.
Experiment with different pricing models like cost-plus, value-based, or psychological pricing to determine which approach works best for your market and product type.
Monitor customer reactions and adjust prices based on demand elasticity . For products with high elasticity, small price changes can have a significant effect on sales volume.
Leverage market research to understand customer willingness to pay and market trends. Conduct surveys, focus groups, or online tests to gather real-time feedback and refine your pricing strategy.
Determining the right price for a product is essential for a business's success, affecting sales, profitability, and market positioning. Businesses should use strategic pricing methods like cost-plus, market research, price elasticity, and value-based pricing to balance costs, customer preferences, and competition. Continuous monitoring and adjustment of prices based on market trends and customer feedback are crucial for maximizing profitability and maintaining a competitive edge. By adopting a thoughtful pricing strategy, businesses can optimize their pricing, drive sales, and ensure long-term success.